Emi Filter Design Software
Electromagnetic interference in analog TV signalElectromagnetic interference ( EMI), also called radio-frequency interference ( RFI) when in the spectrum, is a disturbance generated by an external source that affects an electrical circuit by, or conduction. The disturbance may degrade the performance of the circuit or even stop it from functioning. In the case of a data path, these effects can range from an increase in error rate to a total loss of the data.
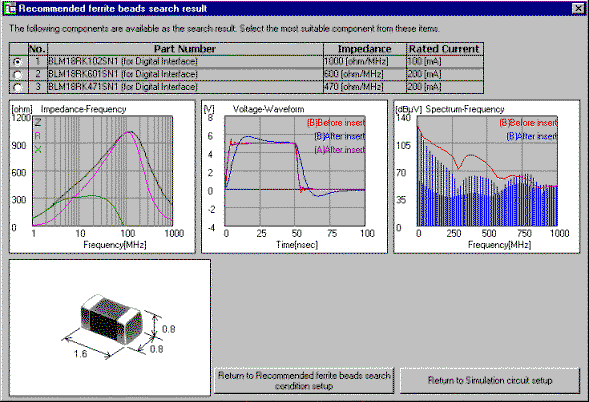
EMI Filter Design - Page 1. EEVblog Electronics Community Forum. A Free & Open Forum For Electronics Enthusiasts & Professionals. Welcome, Guest. And produce representative EMI results without building a prototype; but the software suite to do this costs way more than a few protos and a few weeks of lab time, for most users. Emi Filter Design Software. Design software Creative software discussions and troubleshooting. HyperDrive EMI Filter 3 Shows inside the Macintosh 512k. You can see the EMI filter above the floppy drive at left, and the HD drive mechanism sitting vertically at right, and the power supply in the background.
Both man-made and natural sources generate changing electrical currents and voltages that can cause EMI:, of mobile phones, and (northern/southern lights). EMI frequently affects. It can also affect, and, as well as observations for and.EMI can be used intentionally for, as in. Main article:Integrated circuits are often a source of EMI, but they must usually couple their energy to larger objects such as heatsinks, circuit board planes and cables to radiate significantly.On, important means of reducing EMI are: the use of bypass or on each active device (connected across the power supply, as close to the device as possible), control of high-speed signals using series resistors, and filtering. Shielding is usually a last resort after other techniques have failed, because of the added expense of shielding components such as conductive gaskets.The efficiency of the radiation depends on the height above the or (at, one is as good as the other) and the length of the conductor in relation to the wavelength of the signal component (, or such as overshoot, undershoot or ringing). At lower frequencies, such as 133, radiation is almost exclusively via I/O cables; RF noise gets onto the power planes and is coupled to the line drivers via the VCC and GND pins.
The RF is then coupled to the cable through the line driver as. Since the noise is common-mode, shielding has very little effect, even with. The RF energy is from the signal pair to the shield and the shield itself does the radiating.
Icadmac keygen torrent. One cure for this is to use a or to reduce the common-mode signal.At higher frequencies, usually above 500 MHz, traces get electrically longer and higher above the plane. Two techniques are used at these frequencies: wave shaping with series resistors and embedding the traces between the two planes. If all these measures still leave too much EMI, shielding such as RF gaskets and copper tape can be used. Most digital equipment is designed with metal or conductive-coated plastic cases.RF immunity and testing Any unshielded semiconductor (e.g.
An integrated circuit) will tend to act as a detector for those radio signals commonly found in the domestic environment (e.g. Mobile phones). Such a detector can demodulate the high frequency mobile phone carrier (e.g., GSM850 and GSM1900, GSM900 and GSM1800) and produce low-frequency (e.g., 217 Hz) demodulated signals. This demodulation manifests itself as unwanted audible buzz in audio appliances such as amplifier, amplifier, car radio, telephones etc. Adding onboard EMI filters or special layout techniques can help in bypassing EMI or improving RF immunity.Some ICs are designed (e.g., LMV831-LMV834, MAX9724 ) to have integrated RF filters or a special design that helps reduce any demodulation of high-frequency carrier.Designers often need to carry out special tests for RF immunity of parts to be used in a system. These tests are often done in an with a controlled RF environment where the test vectors produce a RF field similar to that produced in an actual environment.
RFI in radio astronomy Interference in, where it is commonly referred to as radio-frequency interference (RFI), is any source of transmission that is within the observed frequency band other than the celestial sources themselves. Because transmitters on and around the Earth can be many times stronger than the astronomical signal of interest, RFI is a major concern for performing radio astronomy. Natural sources of interference, such as lightning and the Sun, are also often referred to as RFI.Some of the frequency bands that are very important for radio astronomy, such as the at 1420 MHz, are protected by regulation.
This is called. However, modern radio-astronomical observatories such as, and have a very large bandwidth over which they can observe. Because of the limited spectral space at radio frequencies, these frequency bands cannot be completely allocated to radio astronomy. Therefore, observatories need to deal with RFI in their observations.Techniques to deal with RFI range from filters in hardware to advanced algorithms in software. One way to deal with strong transmitters is to filter out the frequency of the source completely. This is for example the case for the LOFAR observatory, which filters out the FM radio stations between 90-110 MHz. It is important to remove such strong sources of interference as soon as possible, because they might 'saturate' the highly sensitive receivers ( and ), which means that the received signal is stronger than the receiver can handle.
However, filtering out a frequency band implies that these frequencies can never be observed with the instrument.A common technique to deal with RFI within the observed frequency bandwidth, is to employ RFI detection in software. Such software can find samples in time, frequency or time-frequency space that are contaminated by an interfering source. These samples are subsequently ignored in further analysis of the observed data. This process is often referred to as data flagging. Because most transmitters have a small bandwidth and are not continuously present such as lightning or (CB) radio devices, most of the data remains available for the astronomical analysis. However, data flagging can not solve issues with continuous broad-band transmitters, such as windmills, or transmitters.Another way to manage RFI is to establish a (RQZ). RQZ is a well-defined area surrounding receivers that has special regulations to reduce RFI in favor of radio astronomy observations within the zone.
The regulations may include special management of spectrum and power flux or power flux-density limitations. The controls within the zone may cover elements other than radio transmitters or radio devices. These include aircraft controls and control of unintentional radiators such as industrial, scientific and medical devices, vehicles, and power lines. The first RQZ for radio astronomy is (NRQZ), established in 1958. RFI on environmental monitoring Transmissions on adjacent bands to those used by passive, such as, have caused interference, sometimes significant. There is concern that adoption of insufficiently regulated could produce major interference issues. Significant interference can significantly impair performance and incur substantially negative economic and public safety impacts.
These concerns led US Secretary of Commerce and NASA Administrator in February 2019 to urge the FCC to cancel proposed, which was rejected. See also.References. Based on the 'interference' entry of The Concise Oxford English Dictionary, 11th edition, online.
Sue, M.K. Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
Retrieved 6 October 2011. Retrieved 21 January 2014. Radio-Sky Journal.
Radio-Sky Publishing. Retrieved 21 January 2014. Radio frequency interference / editors, Charles L. Hutchinson, Michael B. Kaczynski; contributors, Doug DeMaw. Newington, CT American Radio Relay League c1987. Radio frequency interference handbook.
Compiled and edited by Ralph E. Washington Scientific and Technical Information Office, National Aeronautics and Space Administration; was for sale by the National Technical Information Service, Springfield, Va. 1971. ITU Radio Regulations, Section IV. Radio Stations and Systems – Article 1.166, definition: interference. Paglin, Max D.; Hobson, James R.; Rosenbloom, Joel (1999), The Communications Act: A Legislative History of the Major Amendments, 1934-1996, Pike & Fischer - A BNA Company, p. 210,.
Archived from on 16 October 2013. Retrieved 21 January 2014.
Arc Suppression Technologies. Retrieved February 5, 2012. Arc Suppression Technologies. Retrieved February 5, 2012. Smith, Tony (7 November 2012). Retrieved 21 January 2014.
Clemson University Vehicular Electronics Laboratory. Retrieved 21 January 2014. Retrieved 21 January 2014. Fiori, Franco (November 2000). Compliance Engineering. Archived from on 2 March 2012.
Retrieved 21 January 2014. ^ Mehta, Arpit (October 2005). Retrieved 21 January 2014. Retrieved 21 January 2014. 2009-01-07 at the.
Emi Design Guide
(PDF). International Telecommunication Union. September 2012. Retrieved 22 April 2017.
Emi Filter Design Software Free Download
Lubar, David G. (9 January 2019). 15th Annual Symposium on New Generation Operational Environmental Satellite Systems. Phoenix, AZ: American Meteorological Society. Misra, Sidharth (10 January 2019).
15th Annual Symposium on New Generation Operational Environmental Satellite Systems. Phoenix, AZ: American Meteorological Society. Witze, Alexandra (26 April 2019).
Nature News. Brackett, Ron (1 May 2019). The Weather Channel. Samenow, Jason (8 March 2019). The Washington Post. Retrieved 2019-05-05.External links Wikimedia Commons has media related to.
(EMI Tools and Information).